Python 并发请求性能比较
网上很多都是介绍生产者-消费者模型来做并发 所以根据网上例子做一下测试
def Producer():
urls = [
'http://www.python.org',
'https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000000382873',
'http://ddt.8888play.com/news_3935.html',
'http://douban.fm/',
'http://docs.jinkan.org/docs/celery/getting-started/introduction.html',
'http://formspree.io/account',
'http://46.101.85.29/index/#/mz/multipletextsearch/',
'https://pandao.github.io/editor.md/',
'https://www.zhihu.com/question/21343711',
'https://docs.python.org/3/library/queue.html',
'http://www.python.org',
'http://www.python.org',
]
queues = queue.Queue()
pool_size=int(multiprocessing.cpu_count()*0.5)
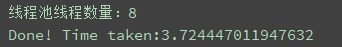
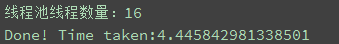
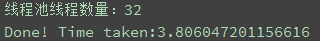
print('线程池线程数量:'+str(pool_size))
worker_threads = build_worker_pool(queues, pool_size)
start_time = time.time()
results = []
for url in urls:
queues.put(url)
for worker in worker_threads:
queues.put('quit')
for worker in worker_threads:
worker.join()
print('Done! Time taken:{}'.format(time.time() - start_time))
def build_worker_pool(queues, size):
workers = []
for _ in range(size):
worker = Consumer(queues)
worker.start()
workers.append(worker)
return workers
if __name__ == '__main__':
Producer()
线程池pool_size 分别使用 8,16,32进行测试
测试结果如下图所示
生产者-消费者模型之外还能使用multiprocessing中的pool来进行并发请求
import multiprocessing
urls = [
'http://www.python.org',
'https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000000382873',
'http://ddt.8888play.com/news_3935.html',
'http://douban.fm/',
'http://docs.jinkan.org/docs/celery/getting-started/introduction.html',
'http://formspree.io/account',
'http://46.101.85.29/index/#/mz/multipletextsearch/',
'https://pandao.github.io/editor.md/',
'https://www.zhihu.com/question/21343711',
'https://docs.python.org/3/library/queue.html',
'http://www.python.org',
'http://www.python.org',
]
results = []
# starttime = time.time()
# pool = TreadPool(4) # 根据核数进行设置
# results = pool.map(urllib.request.urlopen, urls)
# print('4pool:' + str(time.time() - starttime))
# starttime = time.time()
# pool = TreadPool(8) # 根据核数进行设置
# results = pool.map(urllib.request.urlopen, urls)
# print('8pool:' + str(time.time() - starttime))
starttime = time.time()
pool_size=multiprocessing.cpu_count()*2
pool = TreadPool(pool_size) # 根据核数进行设置
results.append(pool.map_async(urllib.request.urlopen, urls))
print('16pool:' + str(time.time() - starttime))
pool.close()
pool.join()
for i in results:
print (i.get())
以下是4,8,16,32 线程运行的结果
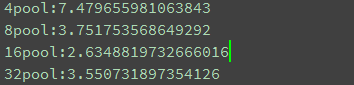
我们发现利用同样的线程数利用python的线程处理库速度明显快一点,而且代码更简洁